What is WannaCry Ransomware : Full Guide

In May 2017, the world witnessed a cybersecurity phenomenon that shook the digital landscape—WannaCry ransomware. Imagine a scenario where critical systems grind to a halt, vital data becomes hostage, and global operations face unprecedented disruption. This is the chilling reality that WannaCry brought to millions of users and organizations. The sheer scale of its impact not only captivated headlines but also ignited a fierce debate about cybersecurity vulnerabilities. As we delve into the intricacies of WannaCry and its aftermath, it becomes evident that understanding this ransomware is crucial for fortifying our defenses against future threats. Don’t miss the chance to uncover how this digital menace evolved into a global crisis.
Table of Contents
What is WannaCry Ransomware?
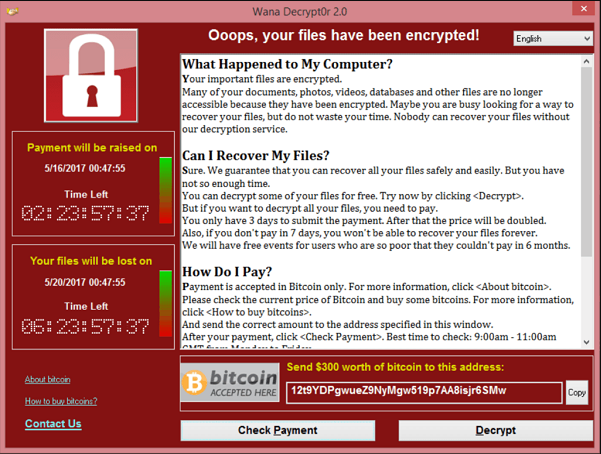
WannaCry ransomware is a pernicious form of malicious software that emerged with alarming speed in May 2017. It encrypts files on an infected computer, rendering them inaccessible to the user and demands a ransom payment in Bitcoin for decryption. This particular strain of ransomware capitalized on a vulnerability in Microsoft Windows known as EternalBlue, which allowed it to spread rapidly across networks. The impact was devastating, affecting thousands of organizations worldwide, from healthcare institutions to private businesses. Understanding WannaCry is crucial for recognizing how such attacks exploit system weaknesses and for developing robust defenses against future ransomware threats.
How It Works and How to Remove It
How It Works?
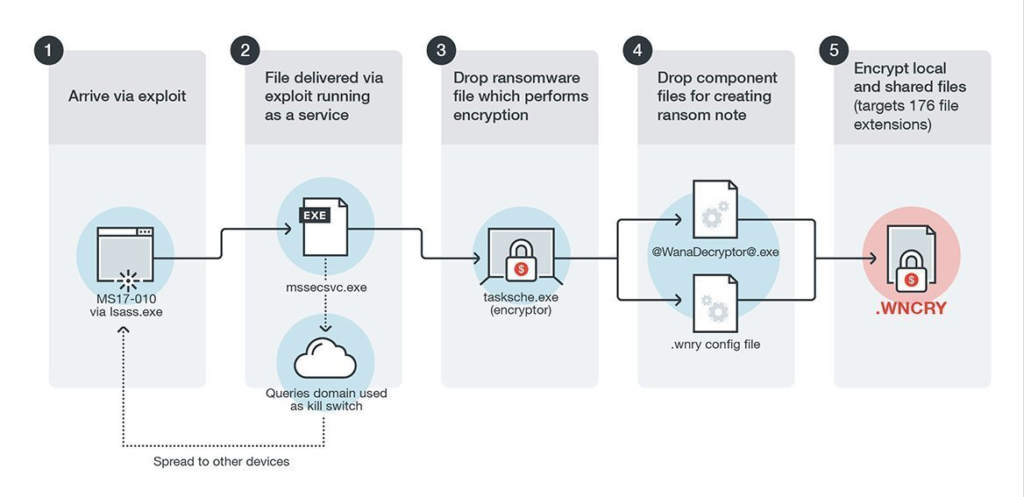
WannaCry ransomware operates by exploiting the EternalBlue vulnerability in Microsoft Windows. Once it infiltrates a system, it encrypts files using a robust encryption algorithm, rendering them inaccessible. Victims are then presented with a ransom demand, usually in Bitcoin, to regain access to their data. The malware spreads rapidly across networks by leveraging the same vulnerability, infecting multiple devices within a short span. This aggressive propagation mechanism allows the ransomware to cause widespread disruption, affecting everything from individual computers to critical infrastructure, making it one of the most notorious cyber threats in recent history.
How to Remove It
Removing WannaCry ransomware requires a meticulous and thorough approach to ensure both the eradication of the malware and the restoration of affected systems. Here is a detailed guide:
- Isolate Infected Systems: Immediately disconnect the infected computer from all networks, including Wi-Fi and Ethernet, to prevent the ransomware from spreading to other devices within the network.
- Boot in Safe Mode: Restart the computer and enter Safe Mode. This limits the operating system to essential functions, preventing the ransomware from executing its encryption processes. Access Safe Mode by pressing F8 (or a similar key) during startup and selecting ‘Safe Mode with Networking.’
- Use Anti-Malware Software: Employ a reputable anti-malware program to perform a comprehensive scan of the system. Tools like Malwarebytes or Windows Defender can detect and remove the WannaCry ransomware. Ensure the anti-malware software is up-to-date to recognize the latest threats.
- Decrypt Files:
- Backup Restoration: If you have reliable backups, restore your data from these secure sources. Ensure that the backups are clean and were created before the infection occurred.
- Decryption Tools: Some cybersecurity firms have developed decryption tools specifically for WannaCry. While not always effective, these tools can potentially decrypt files without paying the ransom. Tools like the WannaKey or WanaKiwi may be useful, but their success depends on specific conditions.
- Update and Patch Systems:
- Install Updates: Ensure that all operating systems and software are fully updated. Microsoft released a patch (MS17-010) that addresses the EternalBlue vulnerability exploited by WannaCry. Installing this patch is crucial to prevent future infections.
- Enable Automatic Updates: Configure your systems to automatically download and install updates, ensuring continuous protection against new vulnerabilities.
- Conduct a Full System Scan: After completing the above steps, perform another comprehensive system scan using your anti-malware software. This ensures that no remnants of WannaCry or other malicious software remain on your system.
- Enhance Security Measures:
- Install a Firewall: Use a robust firewall to monitor and control incoming and outgoing network traffic.
- Use Advanced Security Tools: Consider using tools like intrusion detection systems (IDS) and intrusion prevention systems (IPS) to further protect your network.
- Educate Users: Train employees and users on recognizing phishing attempts and avoiding suspicious emails, links, and attachments, which are common vectors for ransomware.
WannaCry Ransomware Infection Heat Map
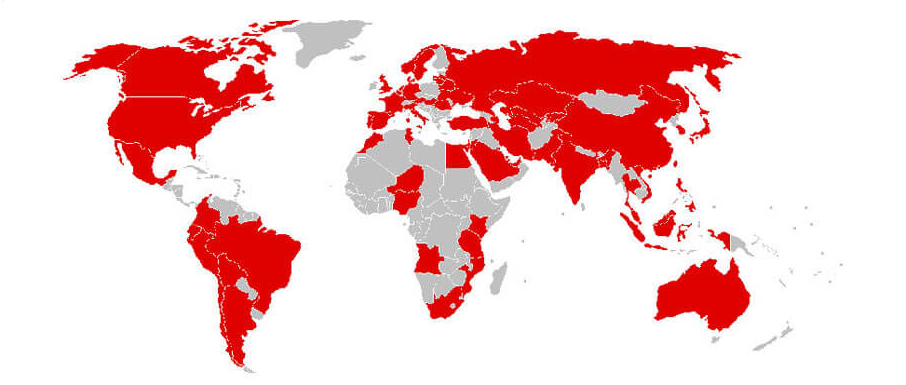
The ransomware infection heat map reveals the extensive reach of this malicious software across the globe. Visual data shows concentrated outbreaks in Europe, particularly in the United Kingdom and Spain, highlighting the vulnerability of critical infrastructure. The heat map also indicates significant infections in Asia and the Americas, demonstrating the widespread impact of the ransomware. This visualization underscores the global nature of cyber threats and the importance of international cooperation in cybersecurity. The heat map serves as a stark reminder of the need for robust defenses and timely updates to protect against such pervasive threats.
What Sectors Were Hardest Hit by WannaCry?
- Healthcare: The National Health Service (NHS) in the United Kingdom was severely affected. Hospitals and clinics experienced widespread disruption, leading to canceled appointments and delayed treatments. Critical patient data became inaccessible, and some emergency departments had to divert patients to other facilities. The attack highlighted the vulnerability of healthcare systems relying on outdated software and underscored the dire need for robust cybersecurity measures in the medical sector.
- Transportation: Major transportation companies saw their operations crippled. Germany’s Deutsche Bahn faced significant challenges as display systems, ticketing services, and customer information systems went offline. This caused widespread confusion and delays in train services, impacting thousands of passengers. The transportation sector’s reliance on interconnected digital systems made it a prime target for the ransomware.
- Telecommunications: Prominent telecommunications firms, including Spain’s Telefónica, were hit hard. Employees were locked out of their workstations, and critical communication services were disrupted. The attack highlighted the risks associated with centralized digital infrastructures and the cascading effects of such disruptions on communication networks.
- Manufacturing: Numerous manufacturing plants faced production halts. Companies such as Renault had to stop production in multiple facilities to prevent the spread of the ransomware. The interconnected nature of modern manufacturing, with systems spanning from assembly lines to supply chain logistics, made these industries particularly susceptible to widespread disruption from WannaCry.
- Government: Government agencies around the world experienced interruptions, with sensitive data becoming encrypted and inaccessible. For instance, the Russian Interior Ministry reported that around 1,000 computers were infected. These breaches compromised critical government functions and data, illustrating the importance of cybersecurity in maintaining national security and public services.
How Many Computers Did WannaCry Infect?
The WannaCry ransomware attack infected an estimated 200,000 computers across more than 150 countries. This unprecedented spread occurred within just a few days, exploiting vulnerabilities in Microsoft Windows systems. The rapid propagation was facilitated by the EternalBlue exploit, which allowed WannaCry to infiltrate networks and encrypt files on a massive scale. The widespread nature of this attack highlighted the critical need for timely software updates and robust cybersecurity measures to protect against such pervasive threats. This incident underscored the importance of global cooperation in addressing and mitigating the impact of ransomware attacks.
What Was the Impact of WannaCry?
- Global Disruption: It caused widespread operational disruptions across various sectors, including healthcare, transportation, and telecommunications.
- Financial Losses: The attack resulted in billions of dollars in damages, from ransom payments to the costs of system restorations and lost productivity.
- Data Inaccessibility: Critical data was encrypted and held hostage, severely affecting services and operations.
- Healthcare Crisis: Hospitals, particularly the NHS in the UK, had to cancel appointments and surgeries, jeopardizing patient care.
- Economic Ripple Effects: Manufacturing plants like Renault faced production halts, impacting supply chains and business operations worldwide.
- Security Wake-Up Call: The attack highlighted significant vulnerabilities in outdated software systems, prompting a global push for improved cybersecurity measures and protocols.
- Government Responses: Many governments were forced to re-evaluate their cybersecurity strategies and invest in stronger defenses.
“In the aftermath of WannaCry, it became clear that regular software updates and robust backup strategies are essential to defend against future ransomware threats.”
Stopping the Spread of WannaCry
1- Strengthen Network Security: Enhancing network security measures, such as implementing firewalls and intrusion detection systems, helped protect against future ransomware attacks and other cyber threats.
2- Isolate Infected Systems: The first step was to disconnect infected devices from networks and the internet. This action helped prevent the ransomware from spreading to other connected systems and limited its impact.
3- Activate the Kill Switch: A significant breakthrough occurred when security researcher Marcus Hutchins discovered a “kill switch” within the ransomware. By registering a domain that ransomware was attempting to contact, Hutchins effectively halted the encryption process, preventing further spread.
4- Deploy Security Patches: Microsoft released emergency security patches for supported and unsupported versions of Windows to address the EternalBlue vulnerability exploited by WannaCry. Organizations and individuals were urged to apply these patches immediately to close the exploit.
5- Run Antivirus Scans: Comprehensive scans using updated antivirus and anti-malware tools were essential to detect and remove any remnants of WannaCry from infected systems.
6- Backup Restoration: For systems that had been compromised but not encrypted, restoring data from clean backups was crucial. Regular backups proved to be a critical line of defense against the effects of WannaCry.
7- Educate and Train Users: Raising awareness about the risks of phishing emails and malicious attachments helped prevent initial infections. Training employees to recognize suspicious activities contributed to reducing the ransomware’s entry points.
Is WannaCry Still a Threat?
As of now, WannaCry is not actively spreading in the same scale as it did during its initial outbreak in 2017. However, the ransomware remains a latent threat. While the immediate crisis was mitigated through patches and countermeasures, vulnerabilities that WannaCry exploited, such as the EternalBlue exploit, continue to pose risks if not addressed. Additionally, variations of WannaCry or similar ransomware could emerge, leveraging the same or new exploits. Thus, maintaining up-to-date security patches, employing robust cybersecurity practices, and staying vigilant are crucial to protecting against potential reinfections or new ransomware threats.
How to Defend Against WannaCry

Defending against WannaCry involves a combination of preventive measures and responsive strategies to safeguard your systems from ransomware attacks. Here’s a comprehensive approach:
- Regular Software Updates: Ensure all operating systems and applications are up-to-date with the latest security patches. Microsoft released critical patches to address the EternalBlue vulnerability exploited by WannaCry. Keeping systems updated closes these security gaps and reduces the risk of infection.
- Use Robust Antivirus Solutions: Deploy comprehensive antivirus and anti-malware software with real-time protection capabilities. Regular scans and updated threat definitions help detect and block WannaCry and similar ransomware before they can execute.
- Implement Network Segmentation: Divide your network into segments to limit the spread of infections. By isolating critical systems and sensitive data, you can contain potential ransomware outbreaks and prevent them from affecting the entire network.
- Backup Data Regularly: Create and maintain regular backups of all critical data. Ensure these backups are stored offline or in a secure cloud environment, separate from the primary network. Regularly test backup restoration procedures to confirm data integrity and accessibility.
- Employ Firewalls and Intrusion Detection Systems: Use firewalls to monitor and control incoming and outgoing network traffic. Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS) can alert you to suspicious activities or potential breaches, allowing for prompt responses to prevent ransomware infections.
- Educate Users: Conduct regular training sessions to educate employees about the risks of phishing emails and malicious attachments. Awareness programs help users recognize and avoid potential threats, reducing the likelihood of initial infection.
- Enforce Strong Password Policies: Implement strong, unique passwords and encourage the use of multi-factor authentication (MFA) to secure accounts and systems. This adds an additional layer of security, making it harder for attackers to gain unauthorized access.
“The WannaCry ransomware attack was a wake-up call for organizations worldwide, emphasizing the dire need for proactive cybersecurity measures.”
Conclusion
In conclusion, the WannaCry ransomware attack serves as a stark reminder of the vulnerabilities inherent in modern digital systems. Its rapid spread and widespread impact underscore the critical importance of robust cybersecurity measures. Regular software updates, comprehensive backups, and user education are essential defenses against such threats. While WannaCry is no longer actively spreading, its legacy highlights the need for continuous vigilance and proactive strategies to safeguard against future ransomware attacks. By implementing these protective measures, organizations can better prepare for and mitigate the risks associated with evolving cyber threats.
“The WannaCry ransomware attack was a wake-up call for organizations worldwide, emphasizing the dire need for proactive cybersecurity measures.”
FAQ on WannaCry Ransomware
1. What is WannaCry? WannaCry is a type of ransomware that encrypts files on infected computers and demands a ransom payment to unlock them. It exploits vulnerabilities in Microsoft Windows systems.
2. How did WannaCry spread? WannaCry spread rapidly through a vulnerability in Microsoft Windows known as EternalBlue. It propagated across networks, infecting computers and encrypting their files.
3. What was the impact of WannaCry? The impact of WannaCry was extensive, affecting over 200,000 computers in more than 150 countries. It disrupted various sectors, including healthcare, transportation, and telecommunications, causing billions of dollars in damages.
4. How can I protect my system from WannaCry? To protect your system from WannaCry, ensure your operating system and software are up-to-date with the latest security patches. Use robust antivirus software, regularly back up your data, and educate users on recognizing phishing emails and malicious attachments.
5. Is WannaCry still a threat? While WannaCry is not actively spreading at the same scale as during its initial outbreak, it remains a latent threat. Unpatched systems are still vulnerable, and variations of the ransomware could emerge.
6. How do I remove WannaCry from an infected system? Removing WannaCry involves isolating the infected system, running comprehensive antivirus scans, and restoring data from clean backups. In some cases, specialized decryption tools may be available to recover encrypted files.