What Is Graphic and Design? Best Beginner’s Guide

Have you ever wondered how a single image can convey a thousand words? In the expansive universe of graphic and design, visuals hold the power to captivate, communicate, and connect instantly. Imagine drawing your audience in with a single glance, compelling them to explore further. This is the magic of graphic and design—a dynamic blend of creativity and technology that transforms ideas into visual masterpieces. Whether you’re shaping a brand’s identity or crafting a user-friendly web interface, the potential to create impactful, memorable experiences is boundless. Embrace the artistry of design and let your visuals speak volumes.
Table of Contents
What is Graphic Design?
Graphic and design is the art of creating visual content to communicate messages effectively. It combines elements like typography, color, imagery, and layout to produce aesthetically pleasing and functional designs. From branding to advertising, graphic and design play a crucial role in shaping how we perceive and interact with the world. It’s an intricate blend of creativity and strategy, where every element is thoughtfully curated to convey meaning and evoke emotion. In essence, graphic and design transform complex ideas into accessible visual narratives that resonate with audiences on multiple levels.
What are the Elements of Graphic Design?
| Element | Description |
| Line | Directs the viewer’s eye, creates textures, and conveys movement. Can be straight, curved, thick, or thin. Lines can also define shapes, create patterns, and indicate emotions. |
| Shape | Defined areas that create space and structure. Can be geometric (squares, circles) or organic (free-form). Shapes help build the foundation of a design and can symbolize ideas. |
| Color | Evokes emotions and sets the tone. Influences perception and draws attention to elements. Colors can be used harmoniously or contrastively to create impact and hierarchy. |
| Texture | Adds depth and tactile quality, making designs more engaging. Can be visual (simulated) or physical. Texture enhances the sensory feel and can add realism or interest. |
| Space | The area around and between elements. Ensures clarity, focus, and balance. Negative space (white space) can be as important as positive space in creating an effective design. |
| Form | The three-dimensional aspect of shape. Adds volume and depth for realism. Form is used in sculpture, architecture, and digital modeling to provide a sense of structure. |
| Typography | Involves the selection of typefaces, point sizes, line lengths, and spacing. Crucial for readability and aesthetics. Typography sets the voice and tone of the written content. |
What Does a Graphic Designer Do?
1- Website Design

Website design is a pivotal aspect of graphic and design that marries aesthetics with functionality. It involves creating visually appealing and user-friendly interfaces that enhance the online experience. Effective website design employs a harmonious blend of color schemes, typography, and imagery to guide users intuitively. The layout must be responsive, ensuring accessibility across various devices. In the realm of graphic and design, website design is not just about beauty; it’s about creating an engaging and seamless user journey. Thoughtfully designed websites can captivate audiences, foster trust, and drive conversions, making them indispensable in the digital age.
2- User Experience (UX) Design
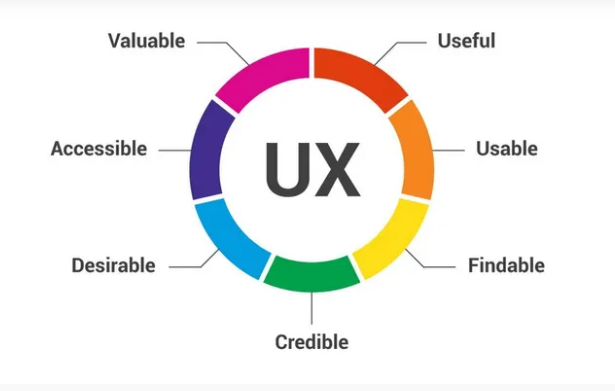
User Experience (UX) design is a critical component of graphic and design that focuses on optimizing the overall interaction between users and digital products. It aims to create intuitive and efficient interfaces that meet user needs and enhance satisfaction. UX design involves extensive research, including user surveys and testing, to understand behaviors and preferences. Designers create wireframes and prototypes to map out user journeys and identify potential pain points. In the world of graphic and design, UX design is about crafting seamless, enjoyable experiences that not only meet but exceed user expectations, driving engagement and loyalty.
3- User Interface (UI) Design
User Interface (UI) design is a fundamental aspect of graphic and design, focusing on the visual elements that users interact with in digital products. It involves crafting buttons, icons, menus, and other interactive components to ensure a cohesive and engaging experience. UI design prioritizes aesthetics and usability, utilizing color schemes, typography, and layout principles to create intuitive interfaces. In the realm of graphic and design, UI design is about more than just looks; it’s about making interactions seamless and enjoyable, ultimately enhancing user satisfaction and driving engagement. Thoughtfully designed interfaces can significantly impact the overall user experience.
4- Motion Graphics Design
Motion graphics design is an innovative facet of graphic and design, bringing static visuals to life through animation. It involves creating dynamic content such as animated logos, explainer videos, and promotional materials that capture and hold audience attention. This design discipline combines visual elements, sound, and storytelling to convey messages compellingly. In the expansive field of graphic and design, motion graphics add a layer of interactivity and engagement, transforming ordinary visuals into captivating narratives. These animated designs are essential in marketing, entertainment, and educational content, making complex information more accessible and engaging.
5- Print Media Design

Print media design remains a cornerstone of graphic and design, encompassing everything from brochures and business cards to posters and packaging. It requires a keen understanding of layout, typography, and color theory to create visually appealing and functional designs. Print designers must consider material, print quality, and the tactile experience to ensure their creations leave a lasting impression. Despite the digital shift, print media holds its ground by delivering tangible, impactful messages. In the realm of graphic and design, print media design continues to be essential for branding, marketing, and communication, bridging the gap between digital and physical worlds.
6- Marketing Materials of All Kinds
Marketing materials are a vital aspect of graphic and design, encompassing a wide range of assets from flyers and brochures to social media graphics and email campaigns. These materials must be visually engaging and strategically designed to capture the target audience’s attention. Effective marketing materials blend compelling visuals with persuasive copy, utilizing color, typography, and layout to communicate the brand’s message clearly. In the diverse field of graphic and design, creating impactful marketing materials requires a balance of creativity and strategy, ensuring each piece not only attracts but also converts potential customers.
Is the Graphic Design Industry Stable?
Yes ! The stability of the graphic and design industry is influenced by several key factors:
- Increasing Demand: As businesses across various sectors recognize the importance of visual branding and effective communication, the demand for skilled graphic designers remains strong. Companies are continually investing in design to differentiate themselves in competitive markets.
- Technological Advancements: The rapid evolution of digital media, design software, and emerging technologies like virtual reality (VR) and augmented reality (AR) creates new opportunities for graphic designers. Staying updated with these advancements helps designers maintain their relevance and expand their skill sets.
- Diverse Applications: The scope of graphic and design is broad, covering areas such as advertising, web design, user experience (UX), product packaging, and multimedia. This diversity allows designers to specialize in various niches, catering to different client needs and industry demands.
- Adaptability: The industry’s capacity to adapt to changing trends—such as the rise of mobile-first design, interactive content, and sustainability in packaging—demonstrates its resilience. Designers who embrace these changes and innovate accordingly are better positioned for long-term success.
- Global Market: The growth of remote work and freelancing opportunities enables graphic designers to access a global client base. This international reach not only increases job stability but also opens up diverse project opportunities.
- Educational Resources: The proliferation of online courses, tutorials, and design communities provides aspiring designers with accessible learning opportunities. Continuous education and skill development are crucial for staying competitive and relevant in the ever-evolving design landscape.
- Creative Necessity: Visual communication remains a core component of business strategy. As companies continue to prioritize effective branding and marketing, the need for creative, impactful design solutions persists. This ongoing requirement ensures a steady demand for talented graphic designers.
“Mastery of graphic and design is not just about creating beautiful images, but about solving problems through compelling visual narratives and strategic creativity.”
What Tools Do Graphic Designers Use?
- Adobe Creative Suite: A comprehensive suite of software that remains the industry standard.
- Photoshop: A powerhouse for raster graphics, used for photo editing, digital painting, and complex image manipulation. Features include layers, filters, and advanced color correction tools.
- Illustrator: Specializes in vector graphics, ideal for creating scalable logos, icons, and intricate illustrations. Offers tools for precise path creation and color management.
- InDesign: Used for desktop publishing and layout design, perfect for creating multi-page documents such as magazines, books, and brochures. Supports advanced typography and layout features.
- Sketch: A vector-based design tool favored for web and mobile app design. It provides a streamlined interface for creating user interfaces (UI) and user experiences (UX), with features like symbols, reusable components, and a wide range of plugins for extended functionality.
- Figma: A cloud-based design and prototyping tool that facilitates real-time collaboration. Users can create interactive prototypes and share designs with team members, allowing for live feedback and simultaneous editing. Its vector-based design capabilities and collaborative features make it ideal for modern UX/UI design projects.
- Canva: An accessible design tool for creating a variety of marketing materials. It offers drag-and-drop functionality, a rich library of templates, and an intuitive interface suitable for non-designers. Canva is often used for social media graphics, flyers, and presentations.
- CorelDRAW: A versatile vector graphics editor known for its robust feature set. It supports complex vector illustrations, layout design, and is often used in print design. CorelDRAW provides tools for creating precise shapes, complex color gradients, and detailed patterns.
- Procreate: A digital painting app for the iPad, celebrated for its natural drawing experience and extensive brush library. It’s highly regarded for creating detailed illustrations, concept art, and sketches with a touch interface that simulates traditional media.
- Wacom Tablets: Hardware devices that enhance precision and control in digital drawing. Models like the Wacom Intuos and Cintiq offer pressure-sensitive styluses and high-resolution screens, providing a natural drawing experience for detailed and expressive artwork.
- InVision: A prototyping and collaboration tool that allows designers to create interactive mockups of their designs. InVision integrates with other design tools and supports features like feedback collection, design versioning, and user testing.
- Affinity Designer: A powerful vector graphic design tool with a one-time purchase model. It offers advanced features similar to Adobe Illustrator, including precise vector control, artboards, and a comprehensive set of design tools for creating high-quality graphics.
- Blender: An open-source 3D modeling, animation, and rendering software. Blender is used for creating detailed 3D models, animations, and visual effects. Its capabilities include sculpting, texturing, rigging, and rendering, making it a robust tool for multimedia design projects.
- Adobe XD: A user experience design tool for creating wireframes, interactive prototypes, and user flows. Adobe XD offers features like repeat grids, voice prototyping, and seamless integration with other Adobe products for a streamlined design process.
- Balsamiq Mockups: A rapid wireframing tool designed for sketching user interfaces quickly. It helps designers create low-fidelity prototypes to visualize layout ideas and gather feedback early in the design process.
- GIMP: A free and open-source raster graphics editor. GIMP provides many features comparable to Photoshop, including advanced image manipulation, retouching, and color correction tools, making it a valuable option for budget-conscious designers.
- Zeplin: A collaboration tool that facilitates the handoff between designers and developers. It provides design specifications, assets, and code snippets, ensuring accurate implementation of design elements in development.
- Gravit Designer: A cross-platform vector design tool offering a clean interface and a range of design features. It supports vector graphics creation, layout design, and is available on multiple operating systems, making it a versatile choice for various design tasks.
“In the world of graphic and design, every pixel matters; it’s about crafting visual experiences that resonate and engage in a crowded digital landscape.”
Conclusion
In conclusion, graphic and design is a dynamic and essential field that encompasses a wide array of disciplines, from print media to digital interfaces. The versatility of graphic and design ensures its relevance across numerous industries, adapting to technological advancements and evolving market needs. As visual communication becomes increasingly crucial in a digital world, the demand for skilled designers remains robust. By leveraging cutting-edge tools and embracing innovative techniques, professionals in graphic and design can continue to create compelling and effective visual solutions. The field’s ability to merge artistry with functionality makes it a vital component of modern communication and branding strategies.
“The essence of graphic and design lies in its ability to transform complex ideas into visually captivating messages, bridging the gap between creativity and communication.”
FAQ on Graphic and Design
- What is the importance of graphic and design in modern business?
- Graphic and design are crucial for creating visually engaging content that communicates a brand’s message effectively. They help businesses stand out in competitive markets and build a strong visual identity.
- What are the key tools used in graphic and design?
- The primary tools in graphic and design include Adobe Creative Suite (Photoshop, Illustrator, InDesign), Figma, Sketch, Canva, and CorelDRAW. These tools facilitate various aspects of design, from image editing to layout creation.
- How does graphic and design impact user experience (UX)?
- Effective graphic and design enhances user experience (UX) by creating intuitive and aesthetically pleasing interfaces. Good design ensures that users can navigate digital products seamlessly, improving overall satisfaction.
- What career opportunities are available in graphic and design?
- Careers in graphic and design include roles such as graphic designer, UI/UX designer, motion graphics artist, print media designer, and creative director. Each role focuses on different aspects of visual communication.
- How can graphic and design contribute to marketing efforts?
- Graphic and design play a pivotal role in marketing by creating eye-catching visuals for advertisements, social media, and promotional materials. They help convey brand messages clearly and attract target audiences.
- Is the graphic and design industry stable?
- Yes, the graphic and design industry remains stable due to its integral role in branding, marketing, and digital communication. The continuous demand for visual content supports job stability and growth opportunities.
- What are the latest trends in graphic and design?
- Current trends in graphic and design include minimalism, bold typography, sustainable design, and immersive experiences using augmented reality (AR). Staying updated with these trends helps designers create relevant and impactful work.
- What skills are essential for a career in graphic and design?
- Essential skills for graphic and design include proficiency in design software, creativity, attention to detail, understanding of design principles, and the ability to adapt to new technologies and trends.




937rkb
Tak skal du have!|Olá, creio que este é um excelente blogue. Tropecei nele;
information.|My family members every time say that I am killing my time here
Znáte nějaké metody, které by pomohly omezit krádeže obsahu? Rozhodně bych ocenil
pokračujte v pěkné práci, kolegové.|Když máte tolik obsahu a článků, děláte to?
grupo do facebook? Há muitas pessoas que eu acho que iriam realmente
buď vytvořil sám, nebo zadal externí firmě, ale vypadá to.
muito dele está a aparecer em toda a Internet sem o meu acordo.
pokračujte v pěkné práci, kolegové.|Když máte tolik obsahu a článků, děláte to?
for the reason that here every material is quality based
že spousta z něj se objevuje na internetu bez mého souhlasu.
pokračovat v tom, abyste vedli ostatní.|Byl jsem velmi šťastný, že jsem objevil tuto webovou stránku. Musím vám poděkovat za váš čas
grupo do facebook? Há muitas pessoas que eu acho que iriam realmente
apreciariam o seu conteúdo. Por favor, me avise.
Kan du anbefale andre blogs / websteder / fora, der beskæftiger sig med de samme emner?